When checking the storage settings, you won’t find anything fishy, yet the issue would have troubled you a lot. Besides, all you can do is move all your important files to a cloud drive and delete them from your system and delete unnecessary ones; thus, only some of the data would remain. Even if sufficient space, the error message pops up again when you try to download anything, and hence you should fix it. While you are thinking of how to do so, we have covered you all!
How to Troubleshoot No Space Left on Device?
There are several methods to resolve the insufficient space issue on Linux. The solutions depend upon the causes which would be responsible for your case. Let’s dig into each one of them. Follow them individually until you find the one that works for you!
Method 1: Release the Space Consumed by Deleted Files
In everyday usage, there are several files that you longer need. Though you delete it afterward, its processes keep running, consuming space. This leads to the No Space Left on Device error on Linux. Since the space isn’t deallocated automatically, therefore you have to deallocate it to resolve the issue. Follow the steps given below to deallocate the space which deleted files are consuming:
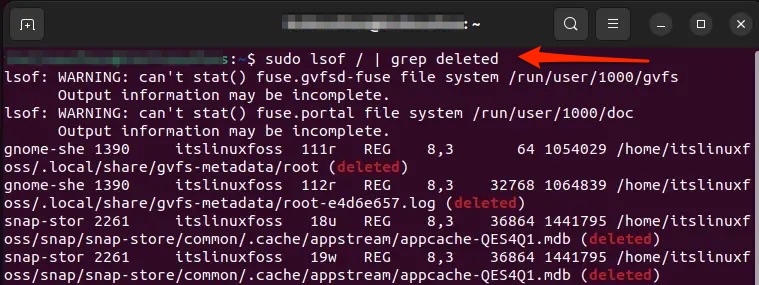
Head over to Terminal. Type the command given below and press the Enter key.
You would now see a list of deleted files whose processes are consuming space.
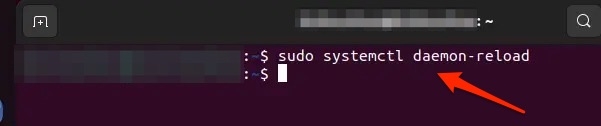
Now, execute the following command to release this space.
Doing so would make a lot of difference, and hence you will eliminate the issue. Besides, you should restart your computer for the changes to reflect.
Method 2: Check the Inodes
There are numerous inodes on a drive, and hence it seems that it won’t won’t out of storage. However, it’s noteworthy that their number is limited. There is quite a possibility that if you have too many files, then too your number of inodes will be occupied even if your drive doesn’t run out of storage. Hence, instead of having multiple small files, you should have larger ones. This is because inodes contain Metadata for the number of files. The more files, the more the Metadata, and so the inodes. A smaller number of files but more extensive data would have lesser inodes. However, before fixing it, you should check whether inodes are the issue! Follow the steps given below to do so:
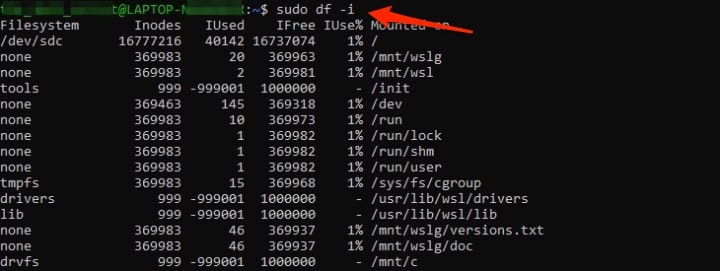
Type the command given below in Terminal and press the Enter key to execute it.
It will display the number of inodes on your computer and those in use. If there is little to no left, then that’s the root cause of the issue. In such a case, you should delete unnecessary files to clear Metadata and hence inodes.
Method 3: Repair the Corrupted Blocks
For various reasons, the storage blocks on your computer get corrupted. Some prominent reasons for these include unutilized blocks on your system leading to the issue. Thus, your Linux OS may not recognize it after a specific time. In such a scenario, you should mark and repair the blocks to troubleshoot the problem. Follow the steps given below to do so:
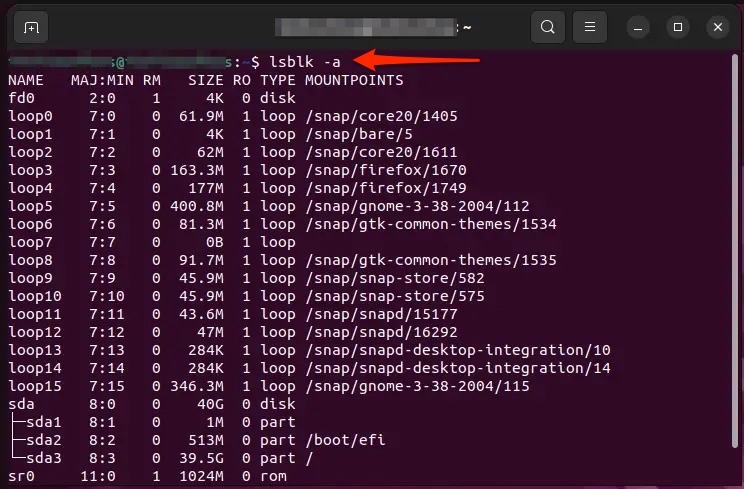
Open the terminal and execute the command given below,
Further, this will generate a list of blocks on your Linux OS.
Type the command and press the Enter key to mark the listed blocks.
You can replace /dev/sda2 with your device name. Linux will again allocate data to these blocks and oversee each so empty ones would be recognized. Since your Linux could recognize the empty blocks, the issue would be resolved. Besides, it will also Repair the Corrupted Blocks. Don’t execute the procedure while a CD is inserted into your computer and is in operation.
How do I resolve a space problem in Linux?
If there’s insufficient space in Linux, you can move your files to a secondary storage device or cloud drive. Besides, you should also compress the larger files.
The Final Verdict – No Space Left on Device Error in Linux
When the No Space Left on Device would have been troubling you, and finding out that you have sufficient space would have puzzled you. It’s often because deleted files’ processes consume much of the storage space leading to the issue. Hence, releasing this space would fix it. Besides, if deleted files aren’t consuming memory, you need to check inodes that contain Metadata for all your files, and since they are finite, they also cause the issue. In such a case, you should delete files you no longer require. Furthermore, Corrupted Blocks can also be the reason, and reporting those would be the ultimate solution. Thus, by following these methods, you will successfully troubleshoot the error. Further Reading:
How to Install and Use iTunes on Ubuntu? Top 5 Best Android Emulators for Linux 7+ Windows Software Alternatives for Linux