“Accidentally deleted an important file? Wiped clean your hard drive? Unsure of what to do with corrupted data? Windows File Recovery can help recover your personal data,” the Store listing for the app explains. “For photos, documents, videos[,] and more, Windows File Recovery supports many file types to help ensure that your data is not permanently lost. Recovering from a camera or SD card? Try Signature mode, which expands beyond NTFS recovery and caters to your storage device needs. Let this app be your first choice for helping to find what you need from your hard drive, SSD (*limited by TRIM), USB drive, or memory cards.” This is a tool that uses the command line to perform all the operations, so this may or may not be compatible for every user out there. This can be used to retrieve data from local hard drives as well as removable media such as USB drives and memory cards. There are three different modes within the applications, as described by Microsoft:
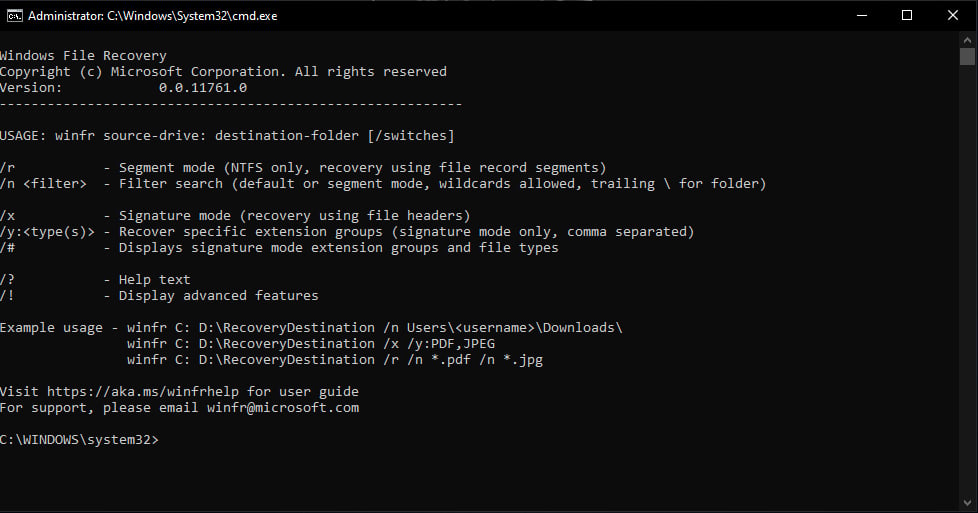
Default mode: This mode uses the Master File Table (MFT) to locate lost files. Default mode works well when the MFT and file segments, also called File Record Segments (FRS), are present.Segment mode: This mode does not require the MFT but does require segments. Segments are summaries of file information that NTFS stores in the MFT such as name, date, size, type, and the cluster/allocation unit index.Signature mode: This mode only requires that the data is present and searches for specific file types. It doesn’t work for small files. To recover a file on an external storage device, such as a USB drive, you can only use Signature mode.
Recover Data using Windows File Recovery Tool
Step 1: Download the exe file or download the tool directly from Microsoft Store (Recommended).
Step 2: Install and Open the Released Windows File Recovery Tool.Step 3: When you are prompted to allow the app to make changes to your device, select Yes.Step 4: In the Command Prompt window, enter the command in the following format:
The source and destination drives must be different. When recovering from the operating system drive (often C: ), use the /n